LLM Personalization
LLM, Huggingface, Scikit Learn, Python, Probabilistic and Neural Retrievers.
Background: I did this project for the COMPSCI 646: Information Retrieval – Fall’23 course at UMass along with Mashrur Rashik. Both authors contributed equally in this project.
Project Title: Improving Retrieval Accuracy Using Clustering to Personalize Large Language Models.
Project Overview: This project focuses on improving the personalization capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by advancing the retrieval of user profile information. By using novel retrieval strategies, including clustering and reranking methods, this project aims to optimize LLM outputs to be more user-specific and contextually relevant.
The project focuses on the following research questions (RQs):
- RQ1: How can relevant information be extracted from a user profile to personalize the output of a Large Language Model (LLM)?
- RQ2: How can the prompt to personalize an LLM output be optimized when the relevant user information is large?
Challenges: This project addresses a suite of challenges related to enhancing the personalization capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) through advanced information retrieval strategies.
-
The core challenge is to extract relevant and significant data efficiently from voluminous and diverse user profiles. This is crucial to ensure that the LLM outputs are both contextually relevant and accurate.
-
The project explores ways to manage large datasets efficiently. It aims to optimize the input sequences for LLMs, making it feasible to process large volumes of data without compromising the quality of the outputs.
-
One of the significant hurdles is enhancing personalization while operating within the bounds of limited computational resources. The project develops retrieval strategies like clustering and reranking that aim to reduce computational demands while maintaining or enhancing performance.
-
Achieving a delicate balance between the accuracy of retrieved information and its relevance to the user's context is challenging. Different models are tested to identify methods that can optimize both aspects effectively.
-
Another challenge is conducting experiments that closely mirror real-world conditions. Using realistic datasets, such as those from the LaMP benchmark, the project validates the effectiveness of different retrieval models in practical scenarios.
Methods: The project used a comprehensive approach to tackle the challenges of personalizing outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs) through information retrieval strategies. Here are the specific solution methods used:
- Use of Various Retrieval Models:
-
BM25 Baseline: Used as a baseline to set a standard for performance comparison with more advanced methods.
-
Topic-Model Based Retrieval: This method uses BM25 to first rank the data points and then incorporates topic modeling to streamline and shorten the input by focusing on key topics rather than full texts.
-
Reranking with Contriever: After initial ranking with BM25, this method uses the Contriever model to rerank the results, aiming to improve relevance by refining the selection of user profile data.
-
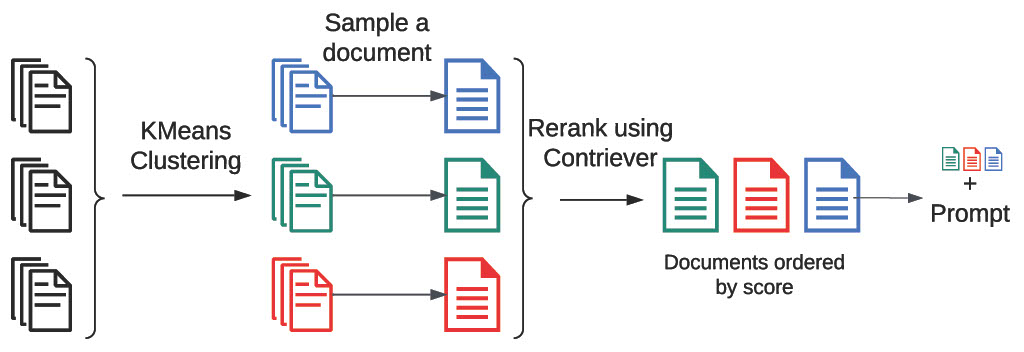
Clustering-Based Retrieval: A novel method where documents are clustered using K-Means clustering, and a representative sample from each cluster is then reranked using Contriever. This approach hypothesizes that it can reduce computational load and improve the relevance of the retrieved documents.
- Integration with Flan-T5-base LLM:
-
The retrieval outputs were integrated as inputs to the Flan-T5-base model to test their effectiveness in generating personalized responses. This step was critical in evaluating how well the retrieved information could be utilized by an LLM in practical scenarios.
Discussion & Findings: The project's findings offer insights to the field of personalized information retrieval for LLMs:
-
Effectiveness of Clustering-Based Retrieval: The clustering-based retrieval method demonstrated promising results, outperforming other techniques in terms of balancing computational efficiency with accuracy and relevance. This suggests that such methods can be particularly useful in scenarios where resources are limited but high personalization is required.
-
Advantages of Reranking Models: The reranking approach using Contriever showed that it could achieve accuracy comparable to the baseline methods while potentially offering better relevance of results due to its ability to dynamically adjust to the context of the query and user profile.
-
Impact of Topic Modeling on Query Efficiency: Topic-model based retrieval was found to be effective in reducing the input size, which could lead to faster processing times. Although it sometimes fell short in accuracy compared to the baseline, it offers a trade-off between efficiency and performance that might be acceptable in certain applications.
-
Scalability and Resource Management: The results highlight the importance of scalable and resource-efficient models in real-world applications. The proposed methods, particularly clustering and reranking, offer ways to manage larger datasets without proportional increases in computational demand.